Injuries resulting in brain trauma are difficult on so many levels. It is very difficult for the victim, the health care providers and your future jurors to understand the extent of your brain injury, an injury that most often is not visible. The Brain Injury Association of Virginia explains that “Brain injury is often called the ‘silent epidemic’ because so many of the problems experienced cannot be seen on an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. Furthermore, many of the observable symptoms are often misinterpreted by both the general public and medical professionals.” In these cases, obtaining legal counsel early in the case can make all the difference. If there is potential compensation available that could ease your financial burden and aid in your recovery, you need to seek it. Please don’t hesitate to call if you or a loved one has suffered a brain injury.
What is brain trauma?
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) – Head injury and brain trauma are synonymous terms, meaning any brain injury produced by an external force.
- Main causes – Car crashes, falls, sports and assaults. This is different from stroke, infection, cancer or other processes that can produce brain “injuries.”
What are the severity levels of TBI?
- Mild – Awake; eyes open. Also called a concussion. Symptoms can include confusion, memory, and attention difficulties, headache, and behavioral problems.
- Moderate – Lethargic; eyes open to stimulation. Some brain swelling or bleeding causing sleepiness, but still arousable.
- Severe – Coma; eyes do not open, even with stimulation. Associated with 20% – 50% death rate or severe disabilities.
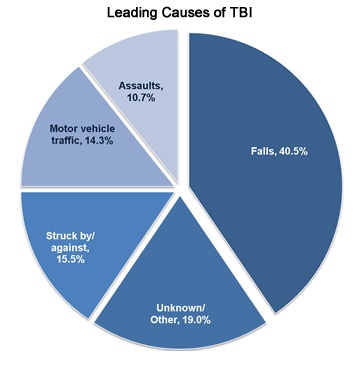
Brain injuries are most often caused by motor vehicle crashes; sports injuries; falls on the playground, at work or in the home; struck by or against events; and assaults.
Every year, approximately 50,000 deaths occur from traumatic brain injury.
An estimated 1.5 million head injuries occur every year in the United States emergency rooms. a
At least 5.3 million Americans, 2% of the U.S. population, currently live with disabilities resulting from TBI.
Moderate and severe head injury (respectively) is associated with a 2.3 and 4.5 times increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Males are about twice as likely as females to experience a TBI.
TBI hospitalization rates have increased from 79% per 100,000 in 2002 to 87.9% per 100,000 in 2003.
aLanglois, J. ScD, MPH; Rutland-Brown, W. MPH; Wald, M. MLS, MPH; The Epidemiology and Impact of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Brief Overview; Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, Vol. 21, No. 5, pp. 375378, 2006
Glossary
Brain death: an irreversible cessation of measurable brain function.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): fluid that bathes and protects the brain and spinal cord.
Closed head injury: an injury that occurs when the head suddenly and violently hits an object but the object does not break through the skull.
Coma: state of profound unconsciousness caused by disease, injury, or poison.
Computed tomography (CT): a scan that creates a series of cross-sectional X-rays of the head and brain; also called computerized axial tomography or CAT scan.
Concussion: injury to the brain caused by a hard blow or violent shaking, causing a sudden and temporary impairment of brain function, such as a short loss of consciousness or disturbance of vision and equilibrium.
Contusion: distinct area of swollen brain tissue mixed with blood released from broken blood vessels.
Intracerebral hematoma: bleeding within the brain caused by damage to a major blood vessel.
Intracranial pressure: buildup of pressure in the brain as a result of injury.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a noninvasive diagnostic technique that uses magnetic fields to detect subtle changes in brain tissue.
Neuron: a nerve cell that is one of the main functional cells of the brain and nervous system.
Penetrating head injury: a brain injury in which an object pierces the skull and enters the brain tissue.
Penetrating skull fracture: a brain injury in which an object pierces the skull and injures brain tissue.
Vasospasm: exaggerated, persistent contraction of the walls of a blood vessel.
Vegetative state: a condition in which patients are unconscious and unaware of their surroundings, but continue to have a sleep/wake cycle and have periods of alertness.
Ventriculostomy: a surgical procedure that drains cerebrospinal fluid from the brain by creating an opening in one of the small cavities called ventricle.
Our goal is to help these victims and their family members reclaim their lives and obtain a sense of justice and financial security. Please contact us at 202-899-5815 to obtain more information about pursuing your legal rights.
There is absolutely no fee to call our office and discuss your unique brain injury with a member of our team. There is no fee for visiting with us and no hourly fee for the time we work on preparing your case, taking discovery and depositions, court appearances, and trial when necessary.
A contingent fee simply means that we do not get paid unless you recover a verdict or settlement. Our attorney fee is contingent upon you getting a recovery. It is a percentage (%) of the amount obtained through settlement or by trial.

